使用NextDenovo软件部分应用文章分享
自软件发布以来,已被众多科研院所、企业等基因测序领域的用户熟知并采用。目前,NextDenovo软件累计下载9200余次,助力发表文章约500篇,高下载量和高引用数体现了NextDenovo软件的高成熟度,成为期刊编辑和审稿人都认可的高质量软件。
为了让更多用户了解NextDenovo的应用案例,小编挑选了6篇具有代表性的文章分享给大家。
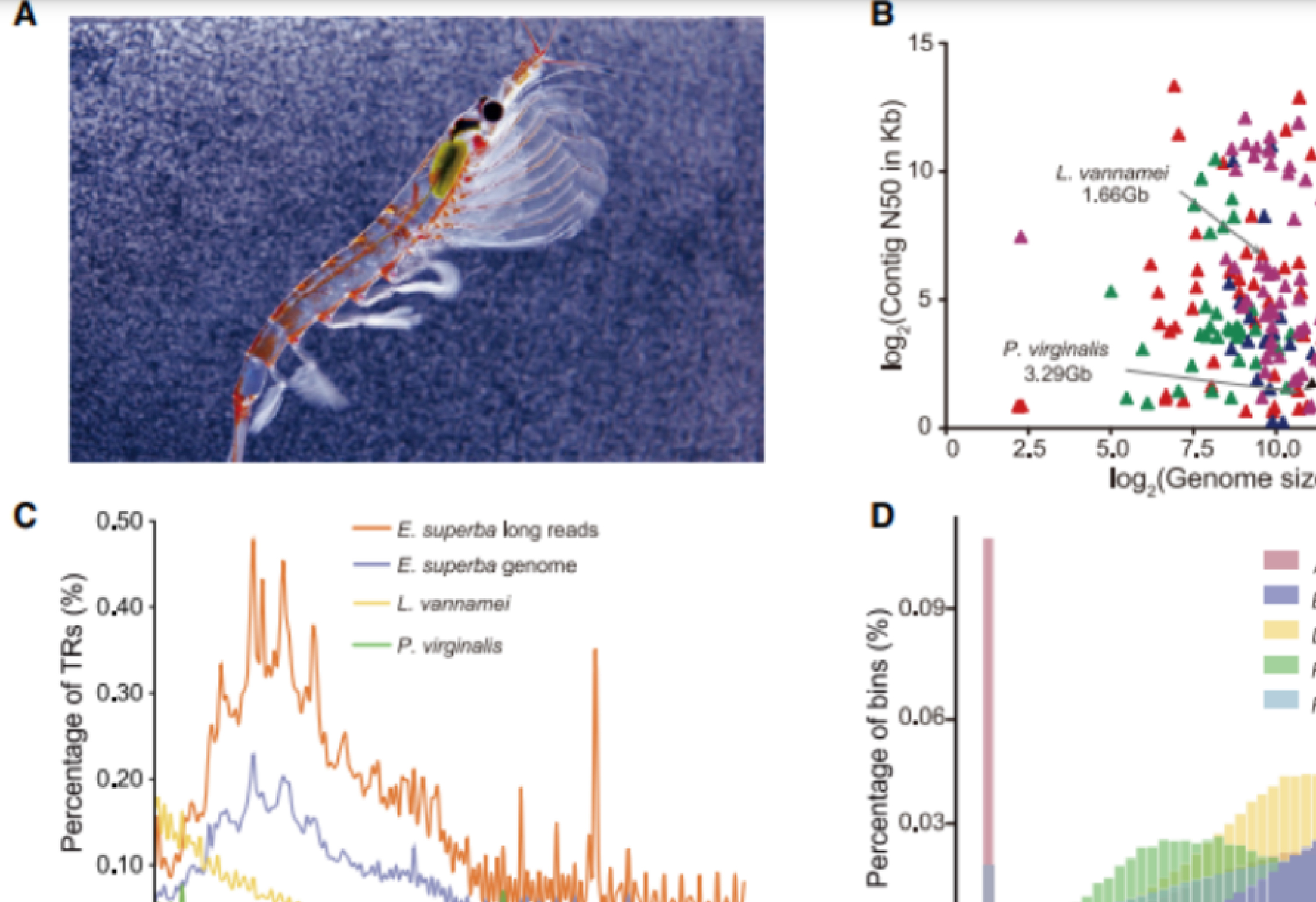
01. The enormous repetitive Antarctic krill genome reveals environmental adaptations and population insights

研究对象:南极磷虾
基因组大小:48G
主要测序技术:Hi-C、PacBio
主要完成单位:中国水产科学研究院黄海水产研究所、青岛华大基因研究院、德国阿尔弗雷德•魏格纳研究所、澳大利亚联邦科学与工业研究组织等机构
希望组贡献:提供NextDenovo组装技术支持
SUMMARY: Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) is Earth’s most abundant wild animal, and its enormous biomass is vital to the Southern Ocean ecosystem. Here, we report a 48.01-Gb chromosome-level Antarctic krill genome, whose large genome size appears to have resulted from inter-genic transposable element expansions. Our assembly reveals the molecular architecture of the Antarctic krill circadian clock and uncovers expanded gene families associated with molting and energy metabolism, providing insights into adaptations to the cold and highly seasonal Antarctic environment. Population-level genome re-sequencing from four geographical sites around the Antarctic continent reveals no clear population structure but highlights natural selection associated with environmental variables. An apparent drastic reduction in krill population size 10 mya and a subsequent rebound 100 thousand years ago coincides with climate change events. Our findings uncover the genomic basis of Antarctic krill adaptations to the Southern Ocean and provide valuable resources for future Antarctic research.
02. African lungfish genome sheds light on the vertebrate water-to-land transition

发表期刊:Cell (IF:66.85)
研究对象:非洲肺鱼
基因组大小:40G
主要测序技术:Nanopore1D、BioNano和Hi-C
主要完成单位:西北工业大学生态与环境学院、中国科学院水生生物研究所淡水生态与生物技术国家重点实验室、中国科学院昆明动物研究所遗传资源与进化国家重点实验室等
第一作者:王堃、王俊、朱成龙、杨连东,任彦栋、阮珏、范广益、胡江(希望组)
SUMMARY: Lungfishes are the closest extant relatives of tetrapods and preserve ancestral traits linked with the water-toland transition. However, their huge genome sizes have hindered understanding of this key transition in evolution. Here, we report a 40-Gb chromosome-level assembly of the African lungfish (Protopterus annectens) genome, which is the largest genome assembly ever reported and has a contig and chromosome N50 of 1.60 Mb and 2.81 Gb, respectively. The large size of the lungfish genome is due mainly to retrotransposons. Genes with ultra-long length show similar expression levels to other genes, indicating that lungfishes have evolved high transcription efficacy to keep gene expression balanced. Together with transcriptome and experimental data, we identified potential genes and regulatory elements related to such terrestrial adaptation traits as pulmonary surfactant, anxiolytic ability, pentadactyl limbs, and pharyngeal remodeling. Our results provide insights and key resources for understanding the evolutionary pathway leading from fishes to humans.
03. Reference genome assemblies reveal the origin and evolution of allohexaploid oat

发表期刊:Nature Genetics (IF: 41.31)
研究对象:燕麦
基因组大小:10.76 Gb
主要测序技术:ONT ultralong 和 Hi-C
主要完成单位:四川农业大学、吉林省白城市农业科学院、中国科学院遗传与发育生物学研究所、四川大学、西昌学院、中国农业科学院、武汉希望组生物科技有限公司
希望组贡献:希望组参与组装注释以及部分分析工作
SUMMARY: Common oat (Avena sativa) is an important cereal crop serving as a valuable source of forage and human food. Although reference genomes of many important crops have been generated, such work in oat has lagged behind, primarily owing to its large, repeat-rich polyploid genome. Here, using Oxford Nanopore ultralong sequencing and Hi-C technologies, we have generated a reference-quality genome assembly of hulless common oat, comprising 21 pseudomolecules with a total length of 10.76 Gb and contig N50 of 75.27 Mb. We also produced genome assemblies for diploid and tetraploid Avena ancestors, which enabled the identification of oat subgenomes and provided insights into oat chromosomal evolution. The origin of hexaploid oat is inferred from whole-genome sequencing, chloroplast genomes and transcriptome assemblies of different Avena species. These findings and the high-quality reference genomes presented here will facilitate the full use of crop genetic resources to accelerate oat improvement.
04. “Omics” data unveil early molecular response underlying limb regeneration in the Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis

发表期刊:Science Advances (IF:15.0)
研究对象:中华绒螯蟹
基因组大小:1.67Gb
主要测序技术:ONT、Hi-C和Bionano
主要完成单位:上海海洋大学水产与生命学院
希望组贡献:三代测序组装注释,Hi-C挂载和Bionano光学图谱服务。
Abstract:Limb regeneration is a fascinating and medically interesting trait that has been well preserved in arthropod lineages, particularly in crustaceans. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying arthropod limb regeneration remain largely elusive. The Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis shows strong regenerative capacity, a trait that has likely allowed it to become a worldwide invasive species. Here, we report a chromosome-level genome of E. sinensis as well as large-scale transcriptome data during the limb regeneration process. Our results reveal that arthropod-specific genes involved in signal transduction, immune response, histone methylation, and cuticle development all play fundamental roles during the regeneration process. Particularly, Innexin2-mediated signal transduction likely facilitates the early stage of the regeneration process, while an effective crustacean-specific prophenoloxidase system (ProPo-AS) plays crucial roles in the initial immune response. Collectively, our findings uncover novel genetic pathways pertaining to arthropod limb regeneration and provide valuable resources for studies on regeneration from a comparative perspective.
05. A near-complete genome assembly of Brassica rapa provides new insights into the evolution of centromeres

发表期刊:Plant Biotechnology Journal (IF:13.26)
研究对象:白菜
基因组大小:424.59 Mb
主要测序技术:ONT、Hi-C和Bionano
主要完成单位:中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所
希望组贡献:三代测序组装注释,Hi-C挂载和Bionano光学图谱服务。
Summary: Brassica rapa comprises many important cultivated vegetables and oil crops. However, Chiifu v3.0, the current B. rapa reference genome, still contains hundreds of gaps. Here, we presented a near-complete genome assembly of B. rapa Chiifu v4.0, which was 424.59 Mb with only two gaps, using Oxford Nanopore Technology (ONT) ultra long-read sequencing and Hi-C technologies. The new assembly contains 12 contigs, with a contig N50 of 38.26 Mb. Eight ofthe ten chromosomes were entirely reconstructed in a single contig from telomere to telomere.We found that the centromeres were mainly invaded by ALE and CRM long terminal repeats(LTRs). Moreover, there is a high divergence of centromere length and sequence among B. rapa genomes. We further found that centromeres are enriched for Copia invaded at 0.14 MYA on average, while pericentromeres are enriched for Gypsy LTRs invaded at 0.51 MYA on average.These results indicated the different invasion mechanisms of LTRs between the two structures. In addition, a novel repetitive sequence PCR630 was identified in the pericentromeres of B. rapa.Overall, the near-complete genome assembly,B. rapa Chiifu v4.0, offers valuable tools forgenomic and genetic studies of Brassica species and provides new insights into the evolution of centromeres.
06. The Telomere to Telomere genome of Fragaria vesca reveals the genomic evolution of Fragaria and the origin of cultivated octoploid strawberry

发表期刊:Horticulture Research (IF:7.29)
研究对象:草莓
基因组大小:220.8Mb
主要测序技术:PacBio HiFi、Hi-C和Bionano
主要完成单位:南京农业大学、海南崖州湾种子实验室
希望组贡献:三代测序组装注释,Hi-C挂载和Bionano光学图谱服务。
Abstract:Fragaria vesca, commonly known as wild or woodland strawberry, is the most widely distributed diploid Fragaria species and is native to Europe and Asia. Because of its small plant size, low heterozygosity, and relatively easy for genetic transformation, F. vesca has been a model plant for fruit research since the publication of its Illumina-based genome in 2011. However, its genomic contribution to octoploid cultivated strawberry remains a long-standing question. Here, we de novo assembled and annotated a telomere-to-telomere, gap-free genome of F. vesca ‘Hawaii 4’, with all seven chromosomes assembled into single contigs, providing the highest completeness and assembly quality to date. The gap-free genome is 220,785,082 bp in length and encodes 36,173 protein-coding gene models, including 1153 newly annotated genes. All 14 telomeres and 7 centromeres were annotated within the 7 chromosomes. Among the three previously recognized wild diploid strawberry ancestors, F. vesca, F. iinumae, and F. viridis, phylogenomic analysis showed that F. vesca and F. viridis are the ancestors of the cultivated octoploid strawberry F. × ananassa, and F. vesca is its closest relative. Three subgenomes of F. × ananassa belong to the F.vesca group, and one is sister to F. viridis. We anticipate that this high-quality, telomere-to-telomere, gap-free F.vesca genome, combined with our phylogenomic inference of the origin of cultivated strawberry, will provide insight into the genomic evolution of Fragaria and facilitate strawberry genetics and molecular breeding.
无论您是基于三代数据的首次组装还是以提升基因组质量为出发点的二次组装,NextDenovo都可以帮您实现不同大小物种的基因组组装!而且,NextDenovo对于PacBio和Nanopore数据都有比较好的适用性,可显著提升基因组组装质量!





发表评论
想参加讨论吗?请尽情讨论吧!